Affective Computing
Teach computer how to learn
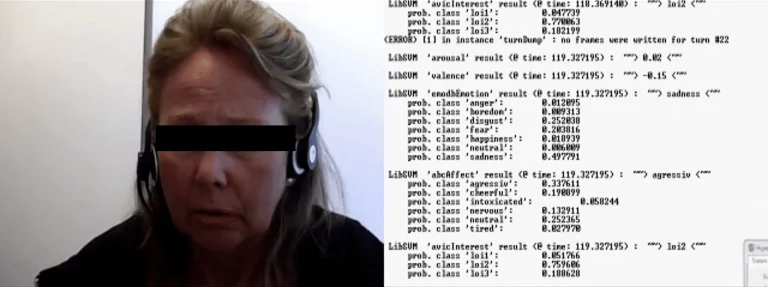
A central aim of affective computing is to quantify aspects of expressive behavior such as facial muscle activations and speech rate in order to detect mood disorders such as depression.
Successful Projects
Development of a screening and support portal as an extensive psycho-social diagnostic mode for refugees
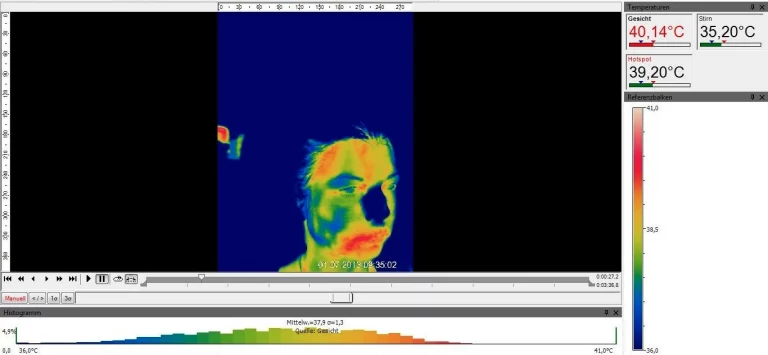
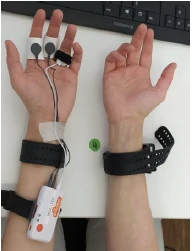
Features extraction of auditory, visual, and physiological data for diagnosis system of affective disorders
A holistic view of interrelated frailties to reduce frailty risk by improving overall well-being
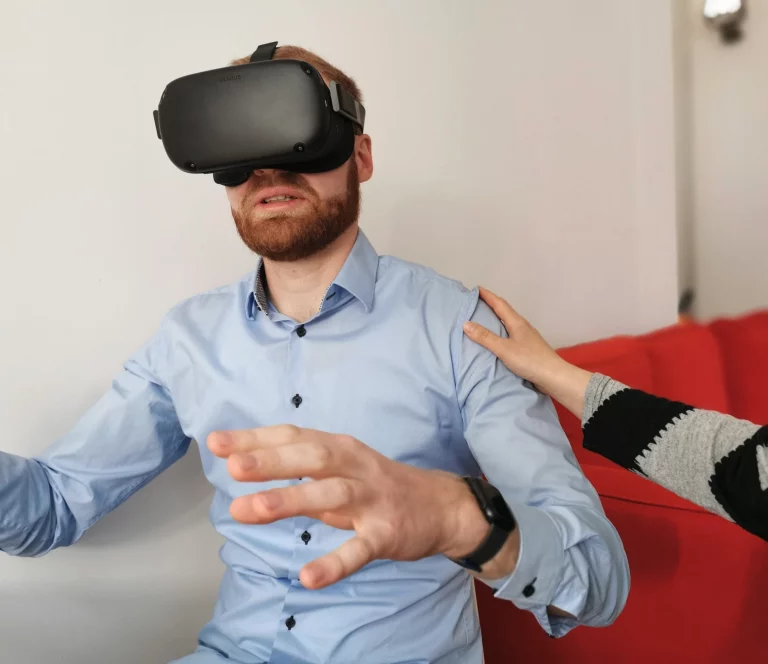
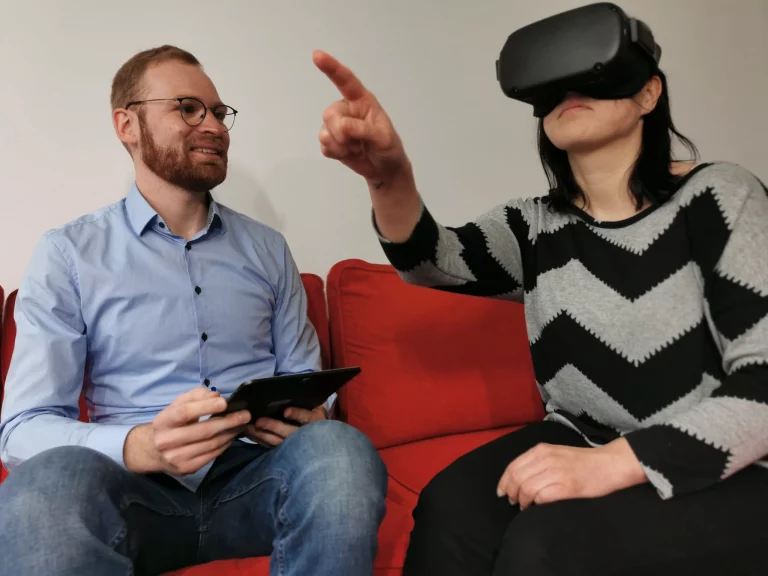
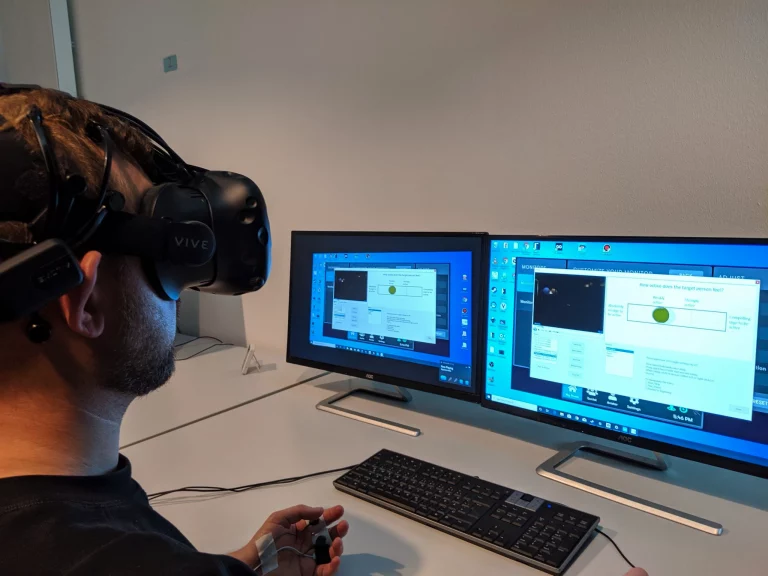
Desktop and virtual reality-supported module variants to bridge waiting times between therapy sessions and enrich ambulant therapy
Support of acute therapy and relapse prevention in the deep psychological treatment
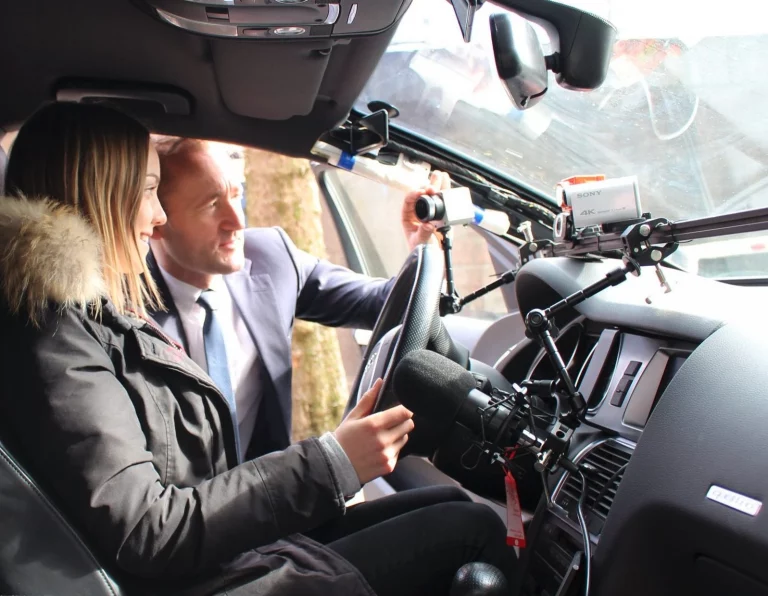
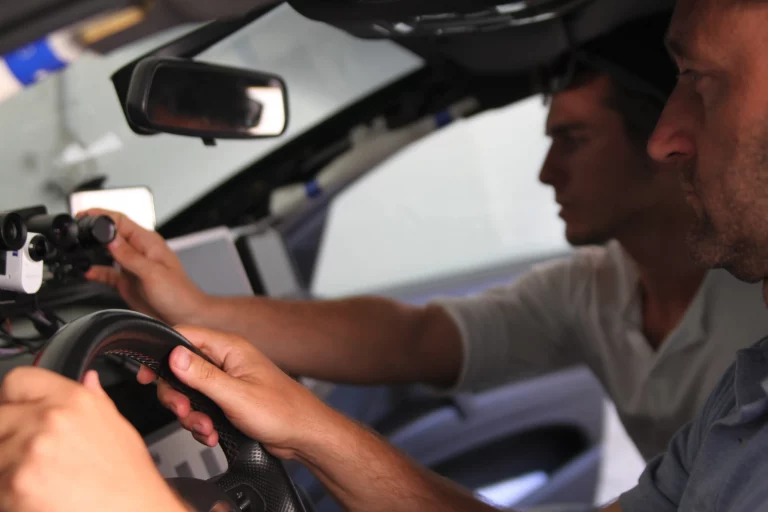
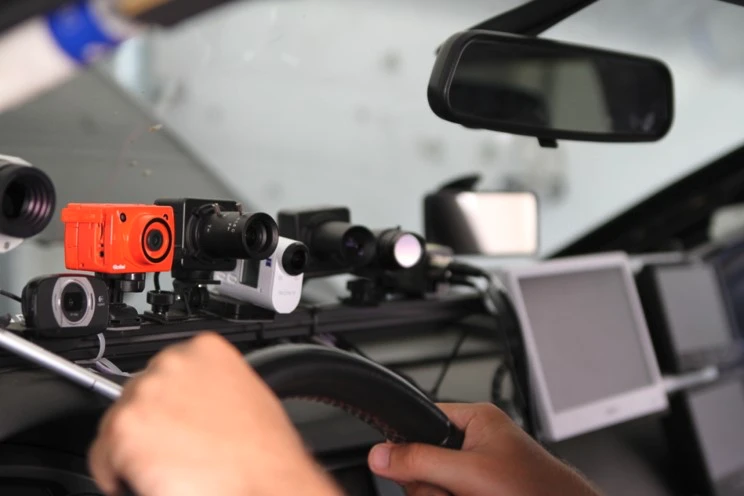
Sudden sickness, distraction, and mind wondering detection by camera and audio based approaches for hand over situations in autonomous driving
Camera-Based Monitoring of Safety-Critical Driver Conditions
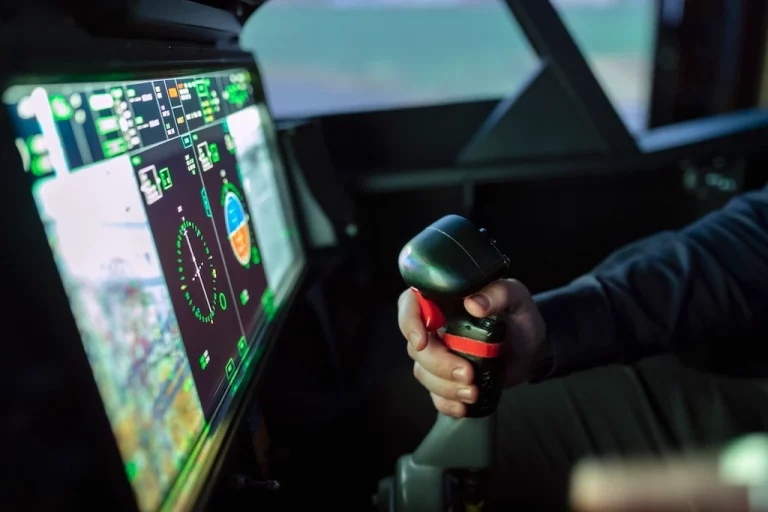
Evaluation of multiple fatigue intervention systems
Multimodal physiological measurements of mental workload for evaluating ADAS
Psychophysiological data collection (EEG, EDA, ECG)
A predictive modelling techniques and pattern recognition-based approach
Computer vision-based detection of attention
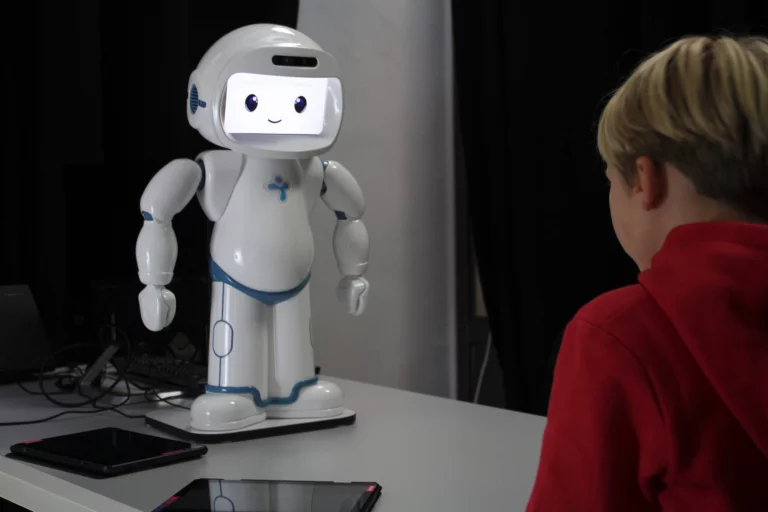
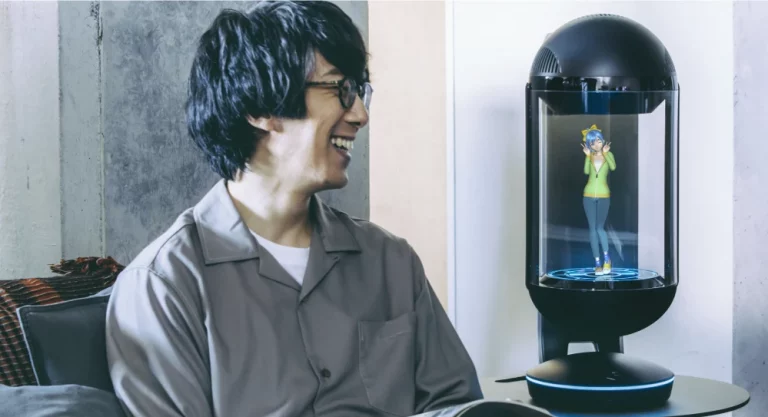
Developing of emphatic dialog systems: an EU-Japanese collaboration