Smart Wearables for Monitoring of Health-Related Behavioral Variables
Improving Health Habits and Life Quality
Project Justification
Wearables such as smartwatches and smartbands are used by a lot of people to track their health status. Information on one’s own health behavior including exercise and sleep activities can shift awareness to this topic and consequently lead to a healthier and more mindful lifestyle.
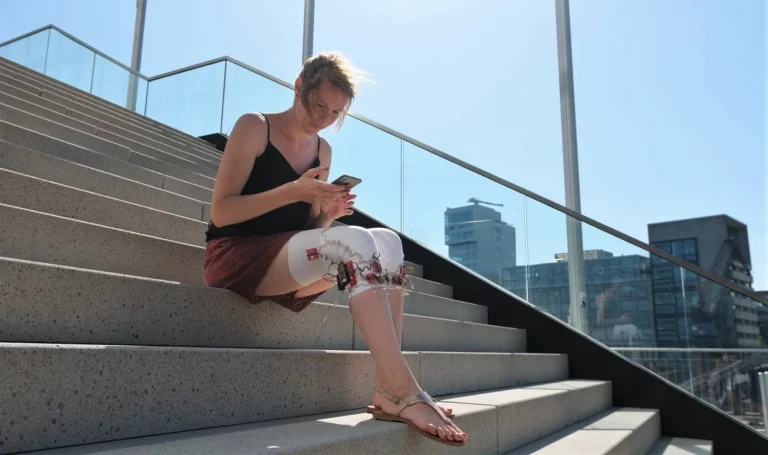
Acceleration data collection in use case 3: Alternate running and walking in 2-minute periods
Our Approach
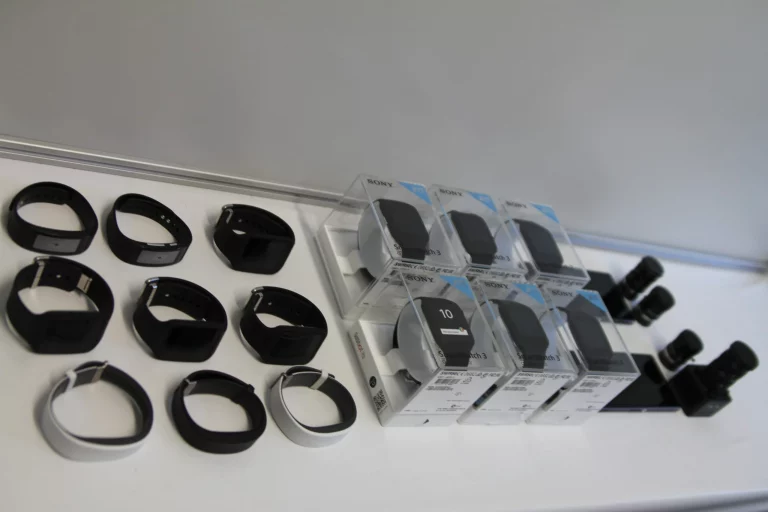
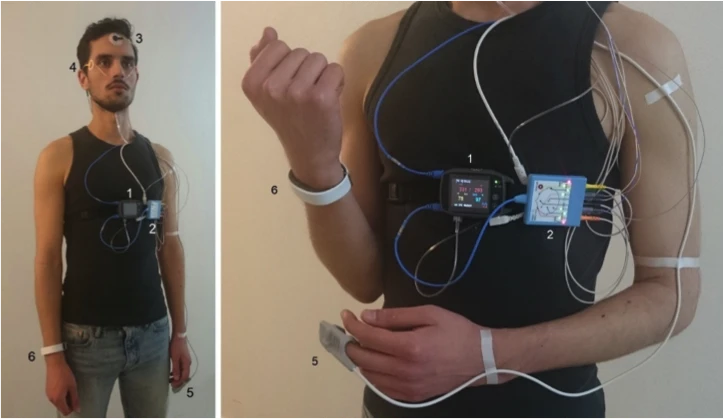
The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of two commercially available smartwatches in tracking heart rate (HR), step count, and sleep stages. The experimental protocol included multiple use cases designed to assess HR accuracy across different cardiovascular intensity zones. For this purpose, participants were instructed to walk and run on a treadmill under controlled laboratory conditions.
To assess sleep stage tracking, participants spent nights in a sleep laboratory, where smartwatch data were directly compared to gold-standard laboratory measurements.
Beyond technical accuracy, user experience was evaluated through a focus group involving exploratory interviews and moderated group discussions. Additionally, to identify potential ergonomic constraints, participants completed several validated questionnaires following a defined habituation period with the devices.
The study provides insight into both the functional validity and user-centered aspects of smartwatch-based health monitoring.
Evaluated smartband
Insights and Outcomes
The results revealed a high correlation between smartwatch and laboratory measurements for heart rate and step count, indicating strong reliability in these domains. Sleep stage detection was found to be fairly accurate, with the devices capturing key sleep markers with acceptable precision.
Insights from the focus group highlighted important aspects of the user experience, particularly regarding the clarity of information presentation, ease of operation, and practicality of charging routines. Overall, the accompanying software of the evaluated smartwatches received consistently positive ratings across multiple user experience dimensions, underscoring their usability and acceptance in everyday health monitoring contexts.
Experimental procedure included several typical use cases to measure accuracy of step counting algorithm. Use cases involved (a) alternate running and walking on a treadmill, (b) walking with suitcase, (c) walking with a smartphone while texting and (d) rest detection during typical office tasks.
Successful Projects
Development of a screening and support portal as an extensive psycho-social diagnostic mode for refugees
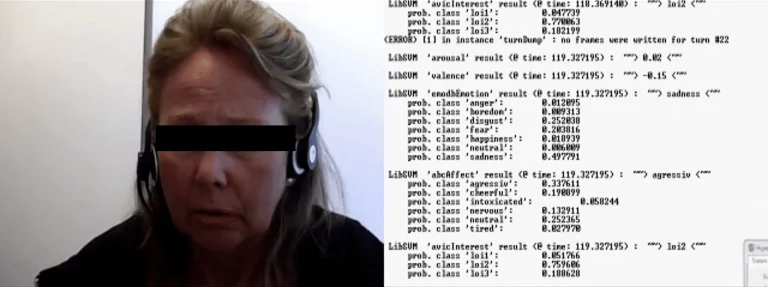
Features extraction of auditory, visual, and physiological data for diagnosis system of affective disorders
A holistic view of interrelated frailties to reduce frailty risk by improving overall well-being
Feedback-assisted rehabilitation after surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament
A contribution of German elite sport to smart health promotion
Market overview, legal and technical requirement analysis, living lab study, and implementation of corporate health management programs
Desktop and virtual reality-supported module variants to bridge waiting times between therapy sessions and enrich ambulant therapy
Support of acute therapy and relapse prevention in the deep psychological treatment