Digital Heath
What is Digital Health?
Digital health is a broad, multidisciplinary field at the intersection of technology and healthcare. It integrates information and communication technologies – including hardware, software, biomedical sciences, and healthcare services – to enhance the efficiency, quality, and personalization of medical care. By leveraging the strengths of each domain, digital health aims to optimize clinical workflows, support patient-centered care, and enable data-informed decision-making across the healthcare continuum.
Digital health technologies are inherently data-driven systems. To ensure reliable, scalable, and ethically sound innovation, it is essential to engage all relevant stakeholders – including patients, healthcare providers, researchers, developers, and policymakers. Only through such inclusive collaboration can digital health systems achieve meaningful progress, promote interoperability, and generate long-term value for public health and individual well-being.
Implications
Innovations in digital health are not solely aimed at reducing time and costs – they are also designed to enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and responsiveness of healthcare information systems. A key advantage lies in the ability to collect health data directly from patients in real-world settings through technologies such as electronic health records (EHRs), electronic medical records (EMRs), and smart wearable devices.
These data streams are processed by digital health platforms using advanced algorithms – including artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques – to extract meaningful insights. The resulting analyses enable the generation of personalized, real-time health recommendations that can be communicated directly to healthcare professionals. This feedback loop supports more precise diagnostics, timely interventions, and tailored care strategies – ultimately contributing to improved clinical outcomes and patient engagement.
Benefits
Digital health technologies have rapidly emerged as a valuable supplement to traditional healthcare delivery. These innovations have become more accessible and affordable than ever before, allowing end users to benefit from functionalities that previously required clinical or hospital-based interventions.
By integrating smart devices, remote monitoring tools, and mobile applications, digital health enables users to track vital parameters, manage chronic conditions, and engage with therapeutic interventions from the comfort of their homes. Such advancements not only save time and reduce healthcare costs – they also improve diagnostic accuracy, treatment efficiency, and overall continuity of care.
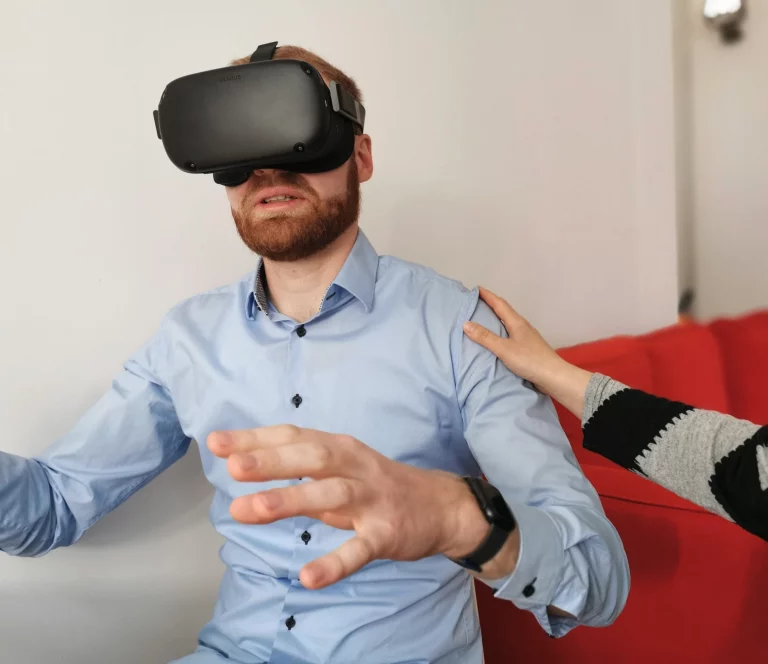
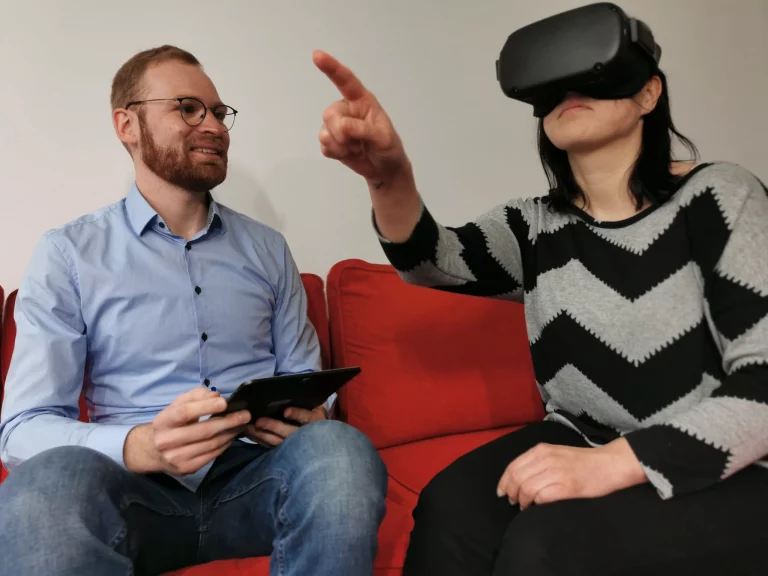
A notable example is the use of virtual reality (VR) as a complementary tool in the treatment of depression, where it has shown promising therapeutic outcomes. As the adoption of these technologies continues to grow, digital health has the potential to bridge critical care gaps – particularly in response to healthcare workforce shortages – and support sustained, patient-centered care during vulnerable or intensive phases of treatment.
Successful Projects
Development of a screening and support portal as an extensive psycho-social diagnostic mode for refugees
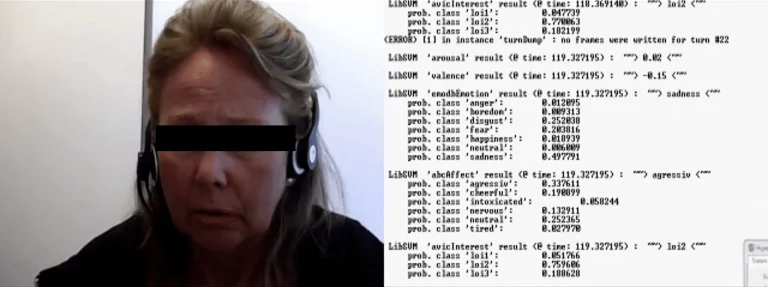
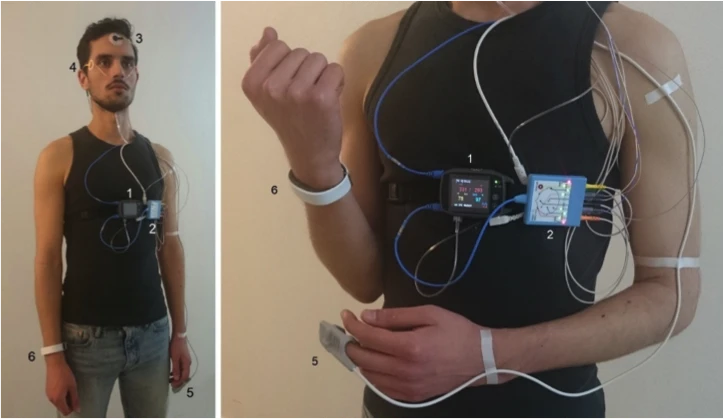
Features extraction of auditory, visual, and physiological data for diagnosis system of affective disorders
A holistic view of interrelated frailties to reduce frailty risk by improving overall well-being
Feedback-assisted rehabilitation after surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament
A contribution of German elite sport to smart health promotion
Market overview, legal and technical requirement analysis, living lab study, and implementation of corporate health management programs
Desktop and virtual reality-supported module variants to bridge waiting times between therapy sessions and enrich ambulant therapy
Support of acute therapy and relapse prevention in the deep psychological treatment