Camera-Based Monitoring of Safety-Critical Driver Conditions
Feasibility Study for the Development of a Deep-Learning-Based Driver Assistance System

Project Justification
The objective of this project was to examine the current state of the art in driver state recognition – and to identify key prerequisites for the acceptance and successful implementation of driver assistance systems.
Safety and comfort remain central features in modern vehicles. As safety standards continue to rise, manufacturers and suppliers are increasingly driven to innovate in the area of advanced driver assistance technologies.
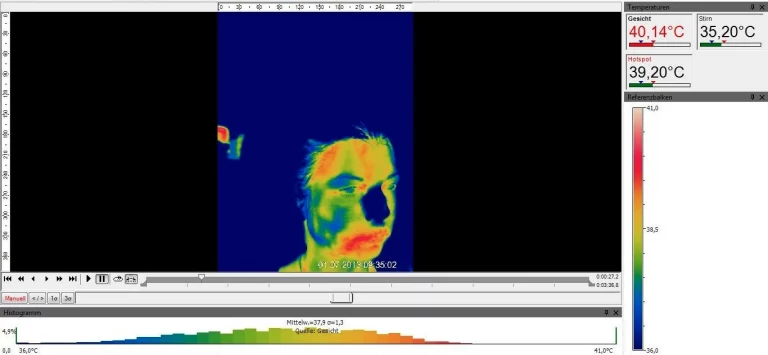
Accurate assessment of the driver’s physical and mental state is a crucial component – particularly in the context of automated driving, where timely and reliable handovers are essential.
In addition to their functional value, comfort- and safety-enhancing sensor systems significantly influence brand perception and differentiation – serving not only to improve user experience but also to strengthen manufacturers’ positions in an increasingly competitive market.
Our Approach
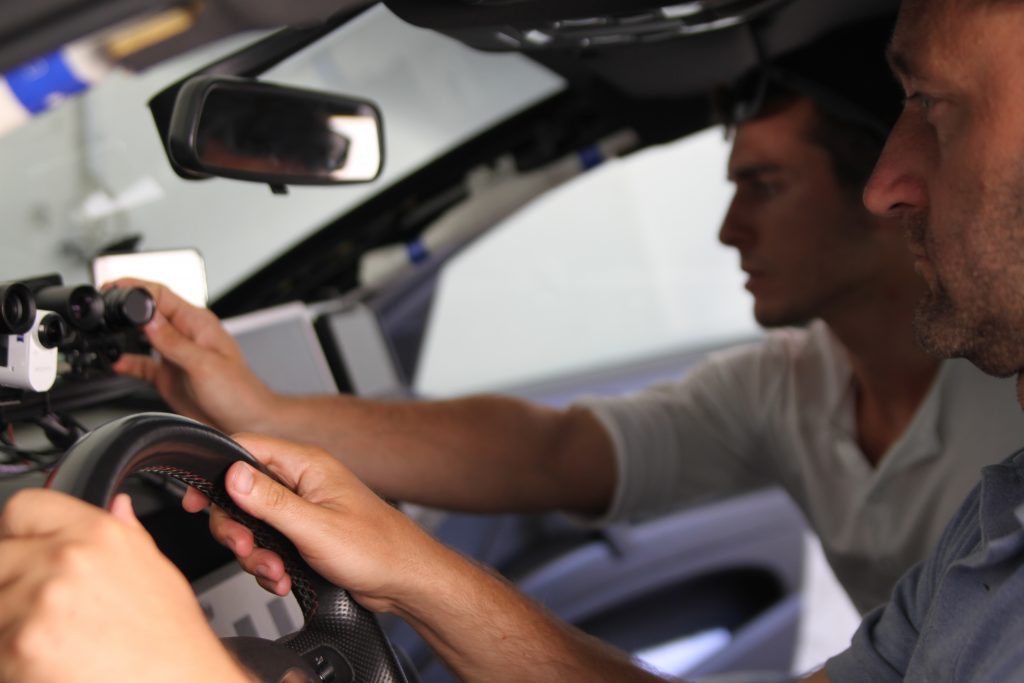
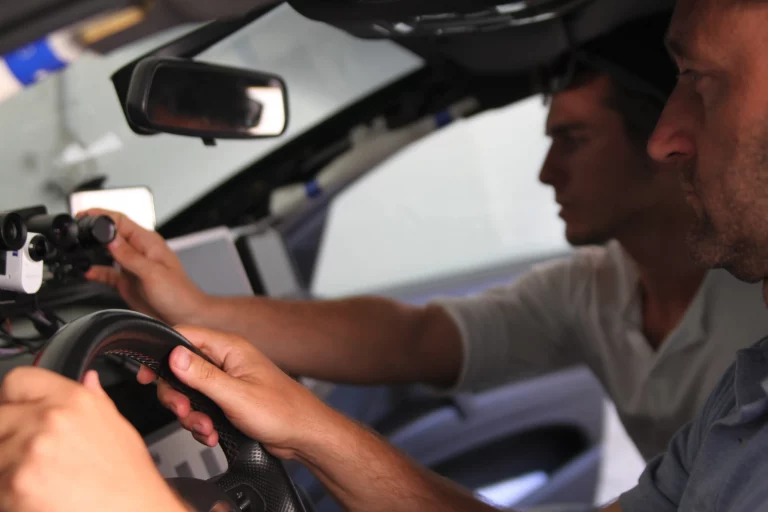
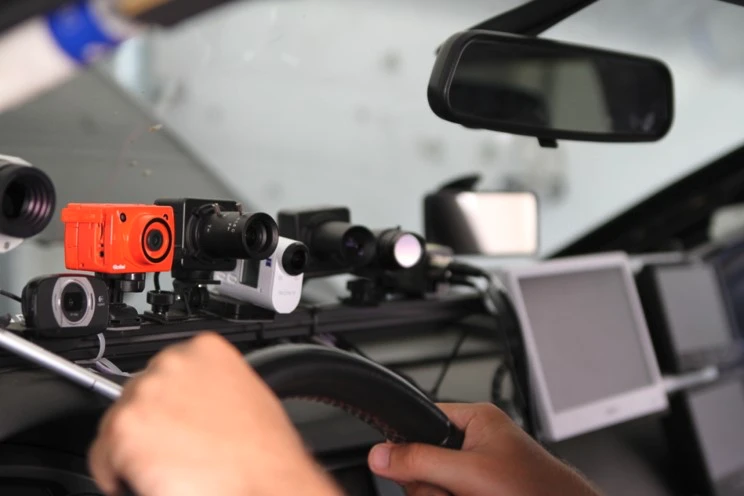
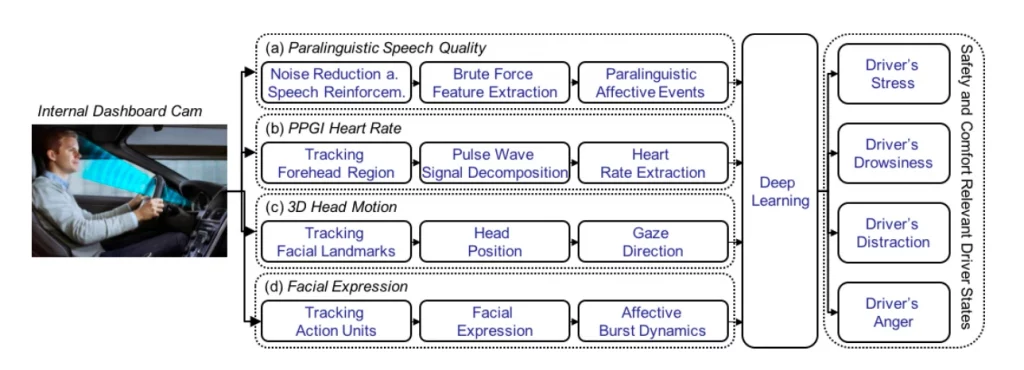
DeepSafeCam aimed to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the feasibility and acceptance of a camera-based driver state assistance system. The project focused on a multifunctional prototype comprising one audio- and three video-based modules, enabling simultaneous, accurate, and robust detection of critical states such as stress, fatigue, distraction, and aggression.
This system is supported by advanced deep learning algorithms capable of real-time data processing and classification of driver states.
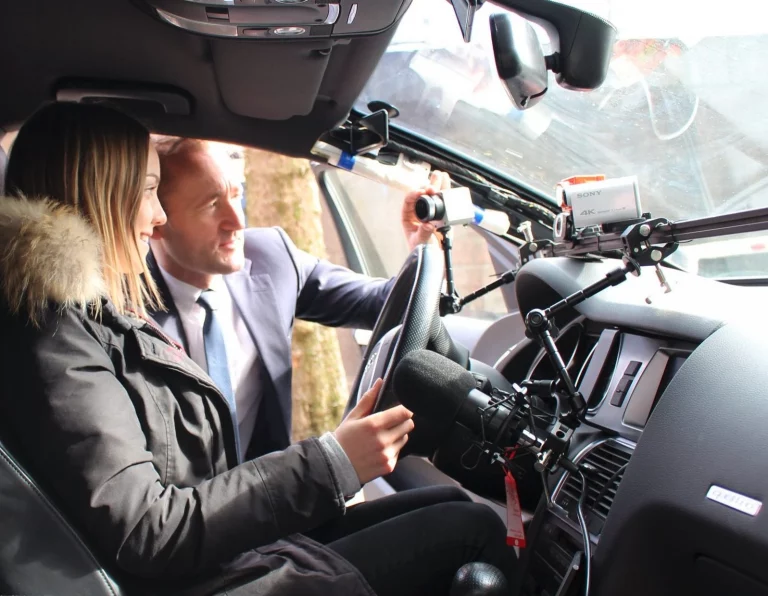
The prototype was assessed through a market analysis, a technological risk evaluation, and a legal framework review. In parallel, user acceptance was investigated using focus groups and validated psychometric instruments – offering insights into both practical applicability and social feasibility.
Prototype for identifying driver states such as fatigue, inattention, and aggression.
Work Packages, Insights and Outcomes
IXP was responsible for conducting a comprehensive market analysis to evaluate customer acceptance of a camera-based driver assistance system. In addition, IXP carried out a technological risk assessment with a focus on non-invasive, accurate, robust, and maintenance-free system architectures.
A further core task was the execution of a legislation risk analysis addressing ethical, legal, and social implications – particularly in relation to data privacy and surveillance concerns.
Overall, the project provided valuable insights into the user-related, legal, and technical requirements necessary for the successful development and implementation of next-generation driver monitoring systems.
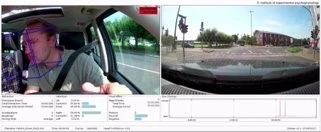
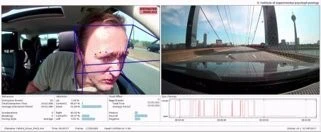


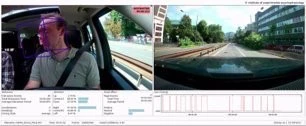
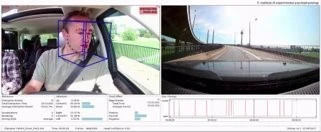

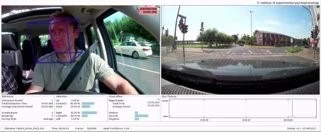
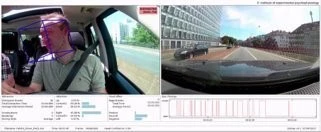
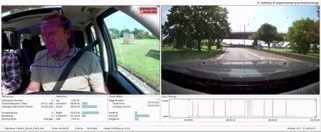
Measurement of distraction by head motion, gaze and blinking during a test drive.
Related Projects
Sudden sickness, distraction, and mind wondering detection by camera and audio based approaches for hand over situations in autonomous driving
Camera-Based Monitoring of Safety-Critical Driver Conditions
Evaluation of multiple fatigue intervention systems
Multimodal physiological measurements of mental workload for evaluating ADAS