Computer Vision
Teach Computers to See
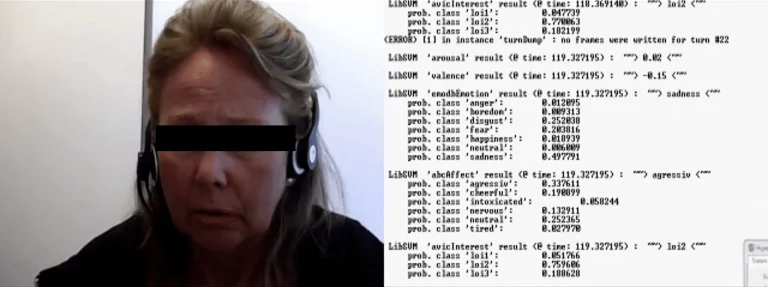
In the field of video-based emotion recognition, the analysis of micro and macro behaviors is essential. Micro behaviors, such as eyelid movements, subtle facial expressions, and fine muscular action units, reveal hidden affective states. For example, anger may be indicated by tightened lips or narrowed eyes, while sadness might manifest in lowered corners of the mouth.
Macro behaviors provide complementary insights, including posture, hand gestures, and locomotor patterns such as pacing or withdrawal. Beyond these, contextual cues – like the presence of potentially dangerous objects (e.g., knives) – offer critical information for assessing situational risks and behavioral intent.
Advancements in automation now allow computer systems to integrate these multimodal signals into robust recognition models. Research demonstrates that micro-level facial muscle activity not only reflects different emotions but can also serve as markers for psychological disorders. At the same time, macro-level behaviors and object detection enrich the interpretative context, enabling more comprehensive and reliable affective computing solutions.
Get an Insight
Playlist

0:16

0:16

0:16




Successful Projects
Development of a screening and support portal as an extensive psycho-social diagnostic mode for refugees
Features extraction of auditory, visual, and physiological data for diagnosis system of affective disorders
A holistic view of interrelated frailties to reduce frailty risk by improving overall well-being
Feedback-assisted rehabilitation after surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament
A contribution of German elite sport to smart health promotion
Market overview, legal and technical requirement analysis, living lab study, and implementation of corporate health management programs
Desktop and virtual reality-supported module variants to bridge waiting times between therapy sessions and enrich ambulant therapy
Support of acute therapy and relapse prevention in the deep psychological treatment
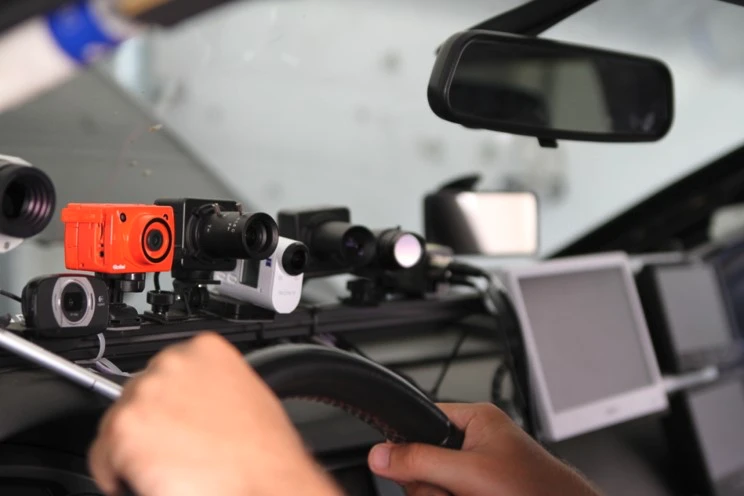
Sudden sickness, distraction, and mind wondering detection by camera and audio based approaches for hand over situations in autonomous driving
Camera-Based Monitoring of Safety-Critical Driver Conditions
Evaluation of multiple fatigue intervention systems
Multimodal physiological measurements of mental workload for evaluating ADAS
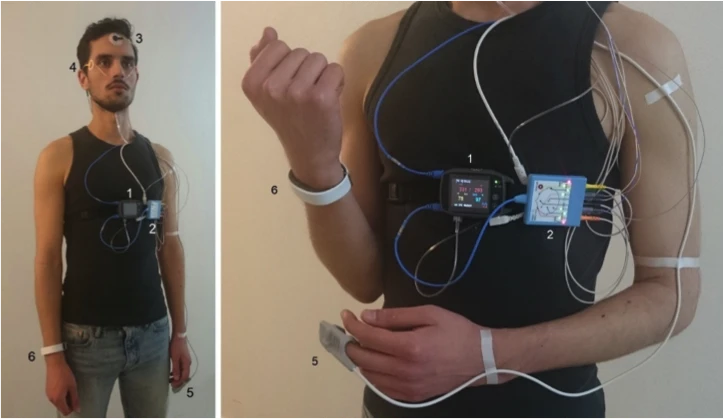
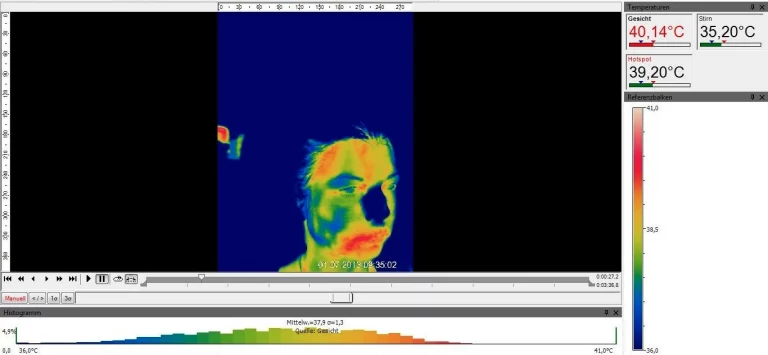
Psychophysiological data collection (EEG, EDA, ECG)
A predictive modelling techniques and pattern recognition-based approach
Computer vision-based detection of attention
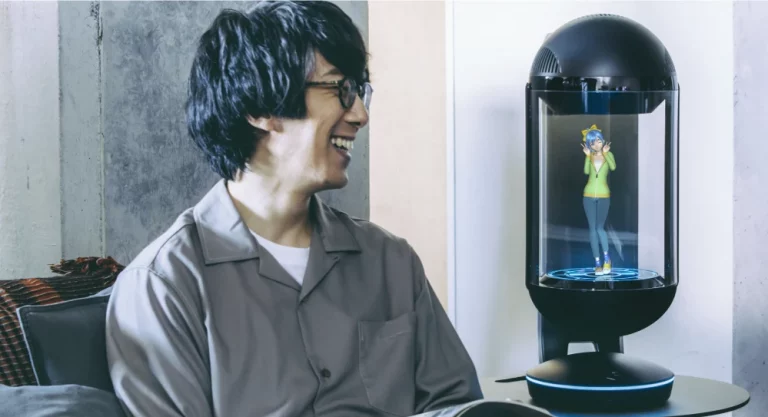
Developing of emphatic dialog systems: an EU-Japanese collaboration